As we all know, a touch screen is an advanced device. It lets users interact with a computer by simply touching the screen. It works by putting special parts, like sensors, inside the display. These sensors detect where you touch. They find the location of your finger or a pen (stylus) and send commands to the computer. So, a touch screen is essentially one device that performs two functions: it serves as both a display and an input tool.
The two most common types of touch screens are resistive and capacitive. Ande Electronics aims to compare these two types of touch screens in terms of structure, working principle, advantages and disadvantages, and typical applications, helping readers quickly understand their differences and uses.
Resistive Touch Screens
The resistive touch screen is one of the most common sensing methods used in the touch screen market before 2010. Besides being used in standalone LCD displays, this technology is also widely used in many small and medium-sized devices.
A resistive screen works by detecting pressure changes on its surface to find the touch position of a finger, stylus, or other object. Its structure is simple: there is a small gap between a glass layer and a film layer, and each layer has a transparent electrode. When the screen is pressed, the electrodes on the film and glass make contact, creating a current. The touch point is then detected by measuring the change in voltage.
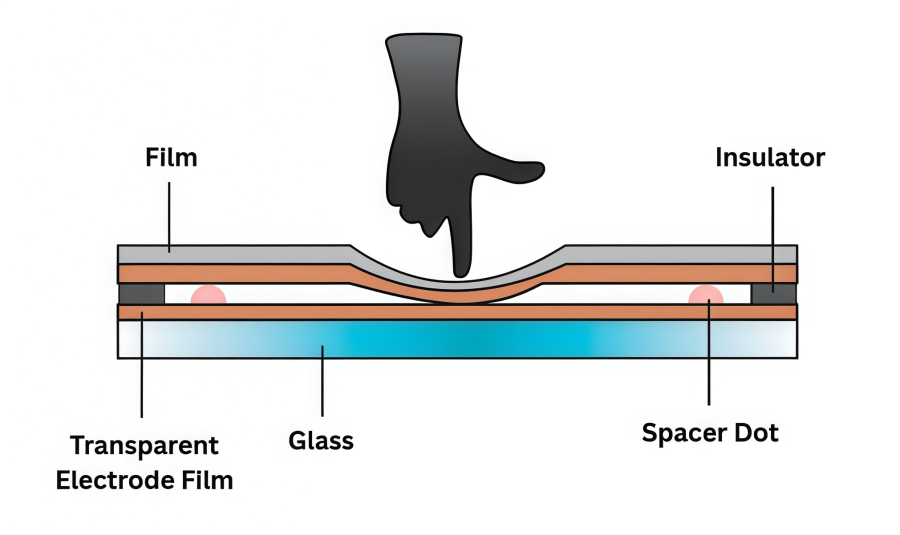
Pros
Simple structure and low manufacturing cost.
Relatively low power consumption.
The surface film design provides good protection against dust and water.
Flexible input methods, including fingers, pens, gloves, etc.
Cons
Lower light transmission.
Relatively limited durability and shock resistance.
Positioning accuracy can be affected on large screens.
Applications
Widely used in early smartphones and feature phones.
Support PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) devices.
Commonly used in car navigation and multimedia control systems.
Used in industrial control panels and medical instruments.
Found in learning devices, POS systems, and handheld gaming consoles.
Capacitive Touch Screens
A capacitive touch screen is one of the most widely used sensing methods after the resistive touch screen. It works by detecting small changes in electric current or capacitance when a finger touches the screen. The sensor reacts to the static electricity of the human body when the finger gets close to the surface, allowing it to detect touch or movement like a pointer on the screen.
There are mainly two types of capacitive touch screens: surface capacitive and projected capacitive. They differ in their internal structure and sensing method.
Surface Capacitive Touch Panel
Surface capacitive touch screens are usually used for relatively large panels. Inside these panels, a transparent electrode film (electrode layer) is placed on a glass substrate and covered by a protective film. Voltage is applied to the electrodes at the four corners of the glass substrate, creating a uniform low-voltage electric field across the panel. By measuring the changes in capacitance at the four corners caused by a finger touch, the screen can detect the touch position.
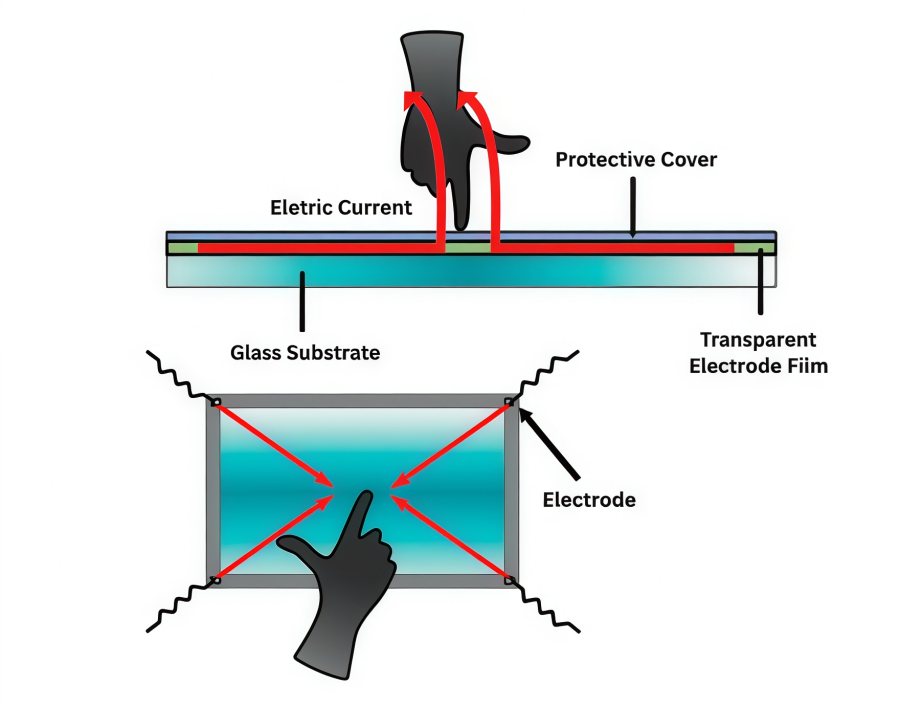
Pros
Simpler structure compared to projected capacitive touch screens.
Light transmittance usually reaches over 90%.
Good scratch and wear resistance.
Cons
Cannot be operated with gloves or non-conductive objects.
Difficult to detect two or more touch points at the same time.
Applications
Applications
Large information displays, such as advertising screens or information kiosks in public places.
Industrial control panels, used for factory or equipment operation interfaces.
Vending machines or self-service terminals, providing simple touch operation.
Medical device display interfaces, suitable for single-touch operation.
Bank self-service machines or ticketing kiosks, for user input and operation.
Projected Capacitive Touch Screen
Projected capacitive touch screens are usually used for smaller screen sizes than surface capacitive touch screens. They are popular in mobile devices. Devices like iPhone, iPod Touch, and iPad use this method to support high-precision multi-touch.
Inside these touch screens, a substrate contains an IC chip for processing. Many transparent electrodes are arranged in a specific pattern on the substrate. The surface is covered with insulating glass or plastic. When a finger approaches, the capacitance between multiple electrodes changes at the same time. By measuring the ratio of these changes, the touch position can be detected accurately.
Pros
Can detect multiple touch points precisely.
High touch sensitivity.
Clear colors and sharp images.
Durable and long-lasting, suitable for frequent use.
Cons
Higher cost and maintenance.
Limited adaptability to different environments.
Applications
Smartphones and tablets, supporting multi-touch operation.
Laptop touchpads, supporting gesture controls.
Touch POS machines and cash registers, improving operation efficiency.
Interactive electronic whiteboards or educational tablets, supporting multiple users at the same time.
High-end car central control screens, providing precise touch experience.
Comparison of Resistive and Capacitive Touch Screen
In this section, we provide a brief comparison of resistive, surface capacitive, and projected capacitive touch screens to help quickly understand their features and applications.
Resistive | Surface Capacitive | Projected Capacitive | |
Principle | Detects pressure | Detects capacitance at corners | Detects capacitance changes across electrodes |
Structure | Glass + film | Electrode film on glass | IC chip + patterned electrodes |
Pros | Low cost, flexible input | Simple, high light transmittance | Multi-touch, high sensitivity, durable |
Cons | Low light, less durable | No gloves, single touch only | Expensive, limited environment use |
Applications | Early phones, PDA, car/nav, industrial, POS | Large displays, industrial panels, kiosks, medical | Smartphones/tablets, laptops, POS, whiteboards, car screens |
Note:
Resistive and capacitive touch screens have different strengths and weaknesses. Resistive screens are simple, low-cost, and can be used with fingers, stylus, or gloves. However, they have lower light transmission, less durability, and are not ideal for multi-touch.
Capacitive screens are more sensitive, support multi-touch, and offer clear images and durability, but they are more expensive and cannot be used with gloves or non-conductive objects. Choosing the right type depends on the device size, usage environment, and touch requirements.
Bonus: Exploring Reliable LCD Touch Screen Solutions
Ande Electronics offers a wide range of hard-to-find LCD screens to help clients complete projects on time. The team provides full support to choose the right touch screen for each project. Customization services are also available for unique applications. Customers can benefit from competitive prices, 24/7 technical support, fast shipping, and strict quality control. With large inventory and strong partnerships with top brands, Ande Electronics delivers reliable and cost-effective LCD solutions.










